The path from RPA to autonomous proxy
A financial crime investigator has received numerous alerts of suspicious activity, requiring tedious investigation efforts to manually collect data across systems in order to phase out false positives and draft other people’s report on suspicious activity (SARS). Today, she obtained priority alerts through automated research and proposed content that could generate SAR in minutes.
A retail category planner previously conducted hours of analysis of reports from the past few weeks to try to reveal insights about which products perform poorly and why AI is now used to provide in-depth insights to surface problem areas and propose Corrective action, prioritize corrective action’s biggest business impact. An industrial maintenance engineer uses a co-pilot to conduct 24/7 asset health monitoring and anticipate problems and issue warnings early in the mechanical or performance issues, thereby reducing unplanned downtime.
These shifts are happening throughout the enterprise, demonstrating the fundamental shift: vertical applications combining predictive, generative and emerging proxy AI are enhancing and transforming workflow automation to deliver targeted, complex features that are compatible with early solutions Compared to solving more complex and contextual challenges.
Gartner’s 2024 emerging technology hype cycle emphasizes that independent AI is one of the four emerging technology trends of that year, and there are good reasons. Using non-AI agents, users must define What They have to be automated how Do this in great detail. However, applications that combine predictive, generative and near-agent AI with dedicated vertical knowledge sources and workflows can get information, speed and automation of repetitive tasks from an enterprise-wide enterprise-wide and for high impact Make suggestions for force movement. Businesses using these applications achieve faster, more accurate decisions, quicker problem identification and remediation, and even preventive measures to prevent problems from happening in the first place.
AI agents represent the next wave in corporate AI. They are based on the basis of predictive and generative AI, but have made significant leaps in autonomy and adaptability. Artificial intelligence agents are not only tools for analysis or content generation, but also intelligent systems that can make independent decisions, solve problems and continue to learn. This advancement marks the transition from AI as a support tool to AI, being able to initiate actions and adapt strategies in real time as an active participant in business processes.
Evolution from RPA to autonomous agent
Traditionally, RPA is used for repetitive, heuristic-based processes and low-complexity tasks with structured data input. RPA uses structured input and defined logic to automate highly repetitive processes such as data entry, transferring files and filling in forms. The wide availability of affordable and efficient predictive and generative AI has addressed the next level of more complex business issues that require domain expertise, enterprise-level security, and the ability to integrate diversified data sources.
At the next level, AI agents go beyond predictive AI algorithms and software, with the ability to operate autonomously, adapt to changing environments, and make decisions based on two pre-programmed rules and learning behaviors. While traditional AI tools may perform well in specific tasks or data analysis, AI agents can integrate multiple functions to browse complex, dynamic environments and solve multiple problems. AI agents can help organizations become more effective, productive, and improve customer and employee experience while reducing costs.
When using the right AI model as a tool as well as vertical data sources and machine learning to support professional contextual activities, AI agents are working on solving problems, taking the right steps to recover from errors and improving outdated AI agents become highly productive jobs Home court. The time for a given task.
Navigation implementation: Key aspects that enterprises need to consider
Implementing predictive, generative, and ultimately proxy AI in an enterprise setup can be extremely beneficial, but taking the right steps to ensure success before deploying is critical. Here are some of the main considerations for businesses to consider and start launching AI agents.
- Align with business goals: To make enterprise AI adoption successful, it should address specific use cases in a specific industry and increase productivity and accuracy. Regularly engage business stakeholders in the AI evaluation/selection process to ensure alignment and provide a clear ROI. Products should be installed in processes and workflows that measurably improve the results of defined use cases and vertical domains.
- Data quality, quantity and integration: Since AI models require a large amount of high-quality data to be effectively executed, enterprises must implement a powerful pipeline of data collection and processing to ensure that AI receives current, accurate, and relevant data. Planning a data source greatly reduces the risk of hallucinations and enables AI to make the best analysis, advice, and decisions.
- Security and Privacy: Processing sensitive data in an AI model poses privacy risks and potential security vulnerabilities. Carefully considering what data AI needs to do its job without providing data that is not directly relevant can help minimize exposure. The application should also provide role-based and user-based access controls, and confirm that SLMS or LLMS is reached without authentication and protection.
- Infrastructure and scalability: Running large AI models requires a lot of computing resources, and scalability can also be a problem. A good design will prevent excessive resource consumption – for example, a professional SLM can be as effective as the more common LLM and significantly reduces computational requirements and latency.
- Model interpretation and explanatory: Many AI models, especially deep learning models, are often regarded as “black boxes.” Good enterprise AI products demonstrate complete transparency, including access to the source of the model, when and why each suggestion is made. Having this context is essential to build user confidence and drive adoption.
Potential drawbacks of AI agents
As with any new technology, AI agents have some potential drawbacks. The best AI proxy applications depend on human processes – including all symphony proxy AI applications and features. This approach allows human supervision, intervention and collaboration to ensure that agents’ actions are aligned with business objectives and ethical considerations. Humans can provide real-time feedback in environmental systems, approve critical decisions, or when they encounter unfamiliar situations, creating strong collaboration between artificial and human intelligence.
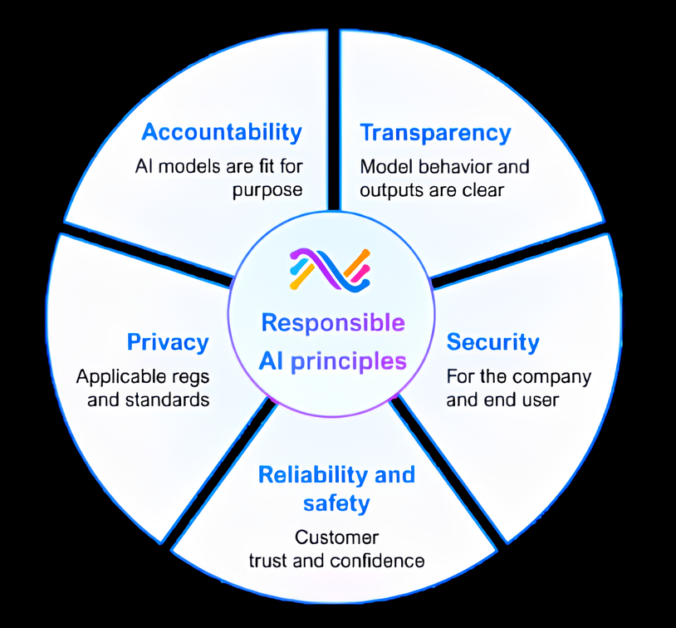
The AI of the person in charge also provides a powerful user interface, traceability, and the ability to review why the agent chooses the steps to execute the path. We adhere to responsible AI responsibilities, transparency, security, reliability/security and privacy principles.
A complete independent agency approach
It is difficult to predict how realistic it is to fully autonomous agency scenarios, as we have not yet established industry-wide measures of the level of autonomy. For example, an autonomous driving area with regard to autonomous driving capabilities level 1-5 has been established, and zero is the level of automation for the driver to perform all driving tasks, while the vehicle performs all driving tasks.
We believe that we think the third phase of the enterprise value path of generative and predictive AI applications combined with AI is well suited. At Symphonyai, we see the next phase of moving towards autonomous AI agents, working with predictive and generative AI to accelerate financial fraud investigations, turbocharged retail category management and demand forecasting and enable manufacturers to predict and avoid machine failures .
We are currently increasing the complexity and autonomy of AI agents in our applications, and customer feedback is very positive. Predictive and generative AI has been improved to the level where workflows can be automated that were once considered too complex for traditional software. Autonomous or proxy AI performs well in handling these tasks without supervision, resulting in transformative productivity gains and allowing HR to focus on more strategic activities.
For example, a transnational European bank using Sympsonyai Sensa Investigation Center with AI agents and Copilot helped financial crime investigators save time on investigations while improving the quality of investigations. In a few weeks, banks’ average efforts to save about 20% in Level 1 and Level 2 surveys. The bank also predicts Symphonyai’s Microsoft Azure will be 3.5 million euros a year, including a 80% reduction in spending from leading technology providers, from 1.5 million euros a year to 300,000 euros a year.
AI Agents use responsible AI principles for thoughtful enterprise-level design, providing transformative productivity, accuracy, and excellence for an increasing number of proven use cases. At Symphonyai, our mission is to provide businesses with operational excellence in AI agents. By integrating fast responsiveness with long-term strategic thinking, proxy AI will revolutionize key processes across multiple industries.


