StepFun AI releases Step-Audio-R1: a new audio LLM that finally benefits from test time calculation extensions
Why current audio AI models tend to perform worse when generating longer inferences rather than making decisions based on actual sounds. The StepFun research team has released Step-Audio-R1, a new audio LLM designed for test-time computing extensions, to address this failure mode by showing that thought chain accuracy degradation is not an audio limitation but a training and modality fundamental issue?
Core Issue, Audio Model Reasoning for Text Agents
Most current audio models inherit the inference behavior of text training. They learn to reason like reading a transcript, not listening. The StepFun team calls this text agent inference. The model uses imagined words and descriptions rather than acoustic cues such as pitch contours, rhythm, timbre, or background noise patterns.
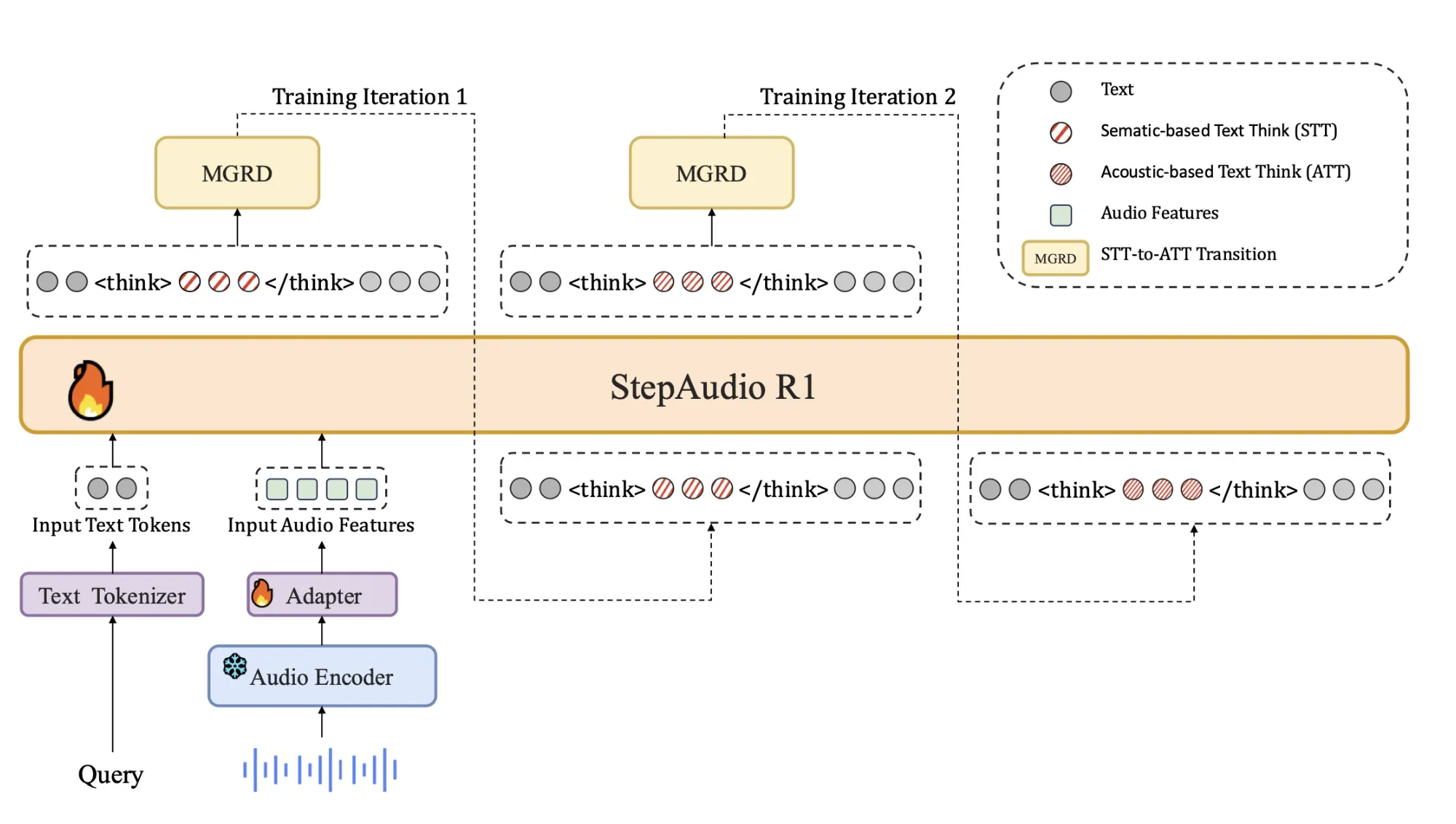
This mismatch explains why longer thought chains often hurt audio performance. The model spends more tokens stating incorrect or modally irrelevant assumptions. Step-Audio-R1 solves this problem by forcing the model to use acoustic evidence to justify the answer. The training pipeline is organized around Modality-Based Reasoning Distillation (MGRD), which selects and extracts inference trajectories that explicitly reference audio features.
architecture
The architecture remains close to previous Step Audio systems:
- The Qwen2-based audio encoder processes the raw waveform at 25 Hz.
- The audio adapter downsamples the encoder output by 2x to 12.5 Hz and aligns the frames with the language markup stream.
- The Qwen2.5 32B decoder uses audio features and generates text.
The decoder always generates explicit inference blocks internally tags, followed by the final answer. This separation lets training objectives shape the structure and content of reasoning without losing focus on task accuracy. The model is released as a 33B parameter audio text to text model on Hugging Face under Apache 2.0.

Training Pipeline, from Cold Start to Audio Grounded RL
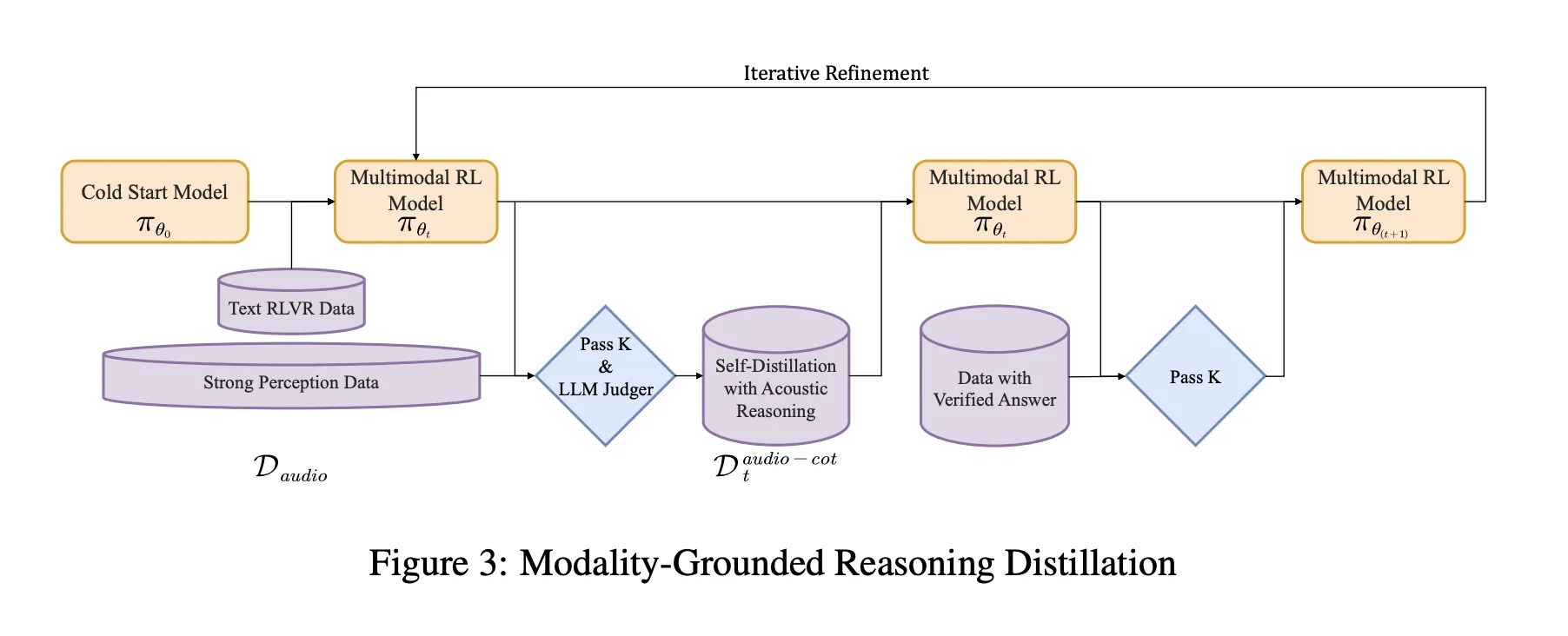
The pipeline has a supervised cold start stage and a reinforcement learning stage that both mix text and audio tasks.
Cold start uses about 5 million examples, covering 1 billion tokens of text only data and 4 billion tokens from audio paired data. Audio tasks include automatic speech recognition, paralinguistic understanding and audio question text answer style dialogs. A fraction of the audio data carries audio chain of thought traces generated by an earlier model. Text data covers multi turn dialog, knowledge question answering, math and code reasoning. All samples share a format where reasoning is wrapped in
Supervised learning trains Step-Audio-R1 to follow this format and generate useful inferences for audio and text. This gives a baseline chain of thinking behaviors, but it still favors text-based reasoning.
Modal based reasoning distillation MGRD
MGRD was applied in multiple iterations. For each round, the research team sampled audio questions where the labels depended on real acoustic properties. For example, questions about the speaker’s mood, background events in the sound scene, or musical structure. Current models generate multiple inferences and answer candidates for each question. The filter retains only chains that satisfy three constraints:
- They cite sonic cues, not just verbal descriptions or imagined transcripts.
- They are logically coherent as short step-by-step explanations.
- Their final answer is correct based on the label or program check.
These accepted traces form a refined dataset of audio thought chains. The model is fine-tuned on this dataset together with raw text inference data. This is followed by reinforcement learning with validation rewards, RLVR. For text questions, rewards are based on correctness of the answer. For audio questions, rewards are a mix of answer correctness and reasoning format, with a typical weight of 0.8 for accuracy and 0.2 for reasoning. Training uses PPO, which samples approximately 16 responses per prompt, and supports sequences of up to approximately 10,240 tokens to allow for long periods of deliberation.

Benchmark test, narrowing the gap with Gemini 3 Pro
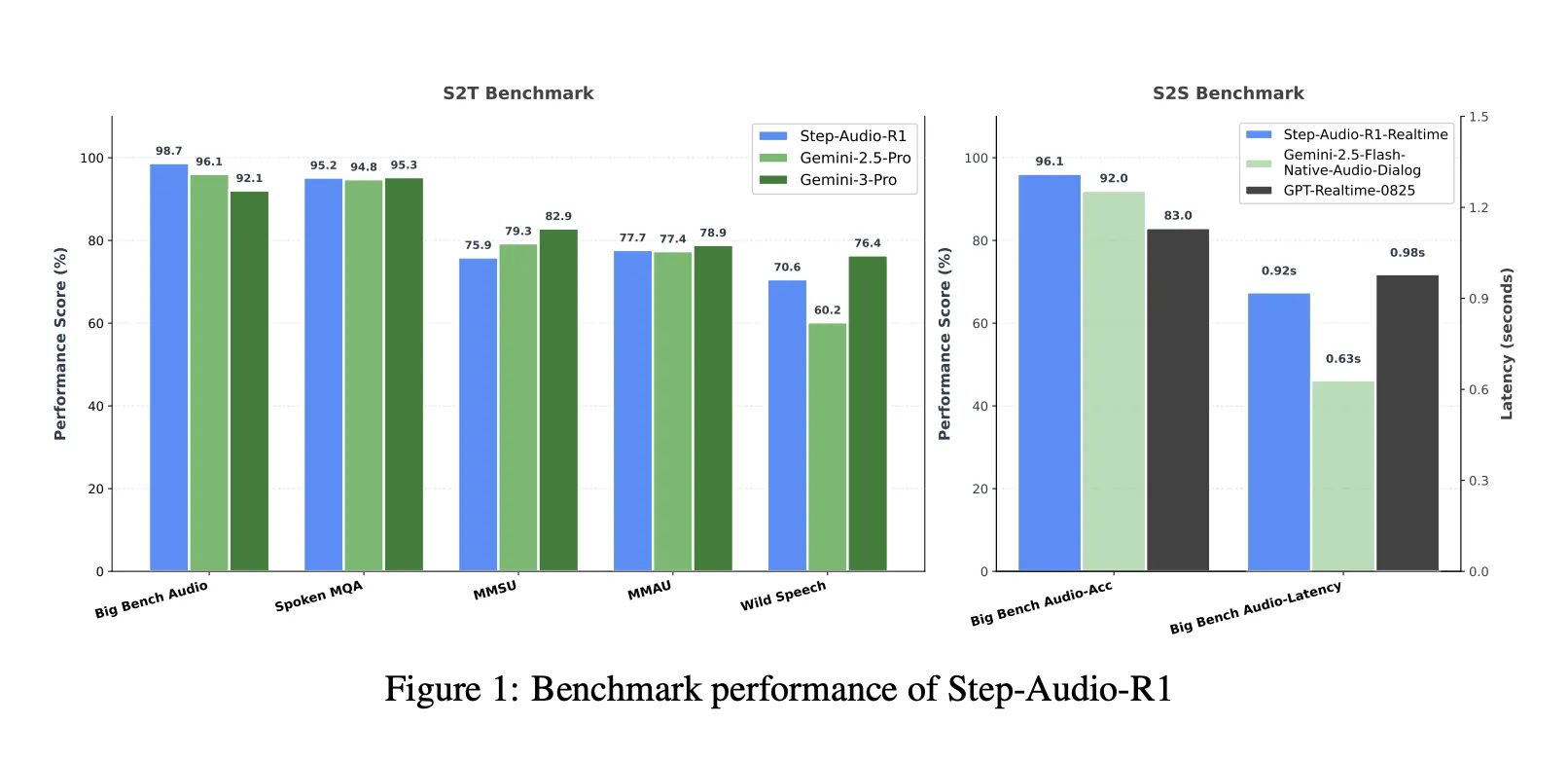
On a comprehensive suite of speech-to-text benchmarks including Big Bench Audio, Spoken MQA, MMSU, MMAU, and Wild Speech, Step-Audio-R1 achieved an average score of approximately 83.6%. The Gemini 2.5 Pro reports about 81.5%, and the Gemini 3 Pro reaches about 85.1%. On Big Bench Audio alone, Step-Audio-R1 reached about 98.7%, which is higher than the two Gemini versions.
For speech-to-speech reasoning, the Step-Audio-R1 Realtime variant features think-while-listening and think-while-speak streaming. On Big Bench Audio speech-to-speech, its inference accuracy is about 96.1%, and the first packet delay is about 0.92 seconds. This score surpasses both the GPT-based real-time baseline and the Gemini 2.5 Flash-style native audio dialog while maintaining sub-second interactivity.

Ablation, what matters most for audio inference
The ablated portion provides engineers with several design signals:
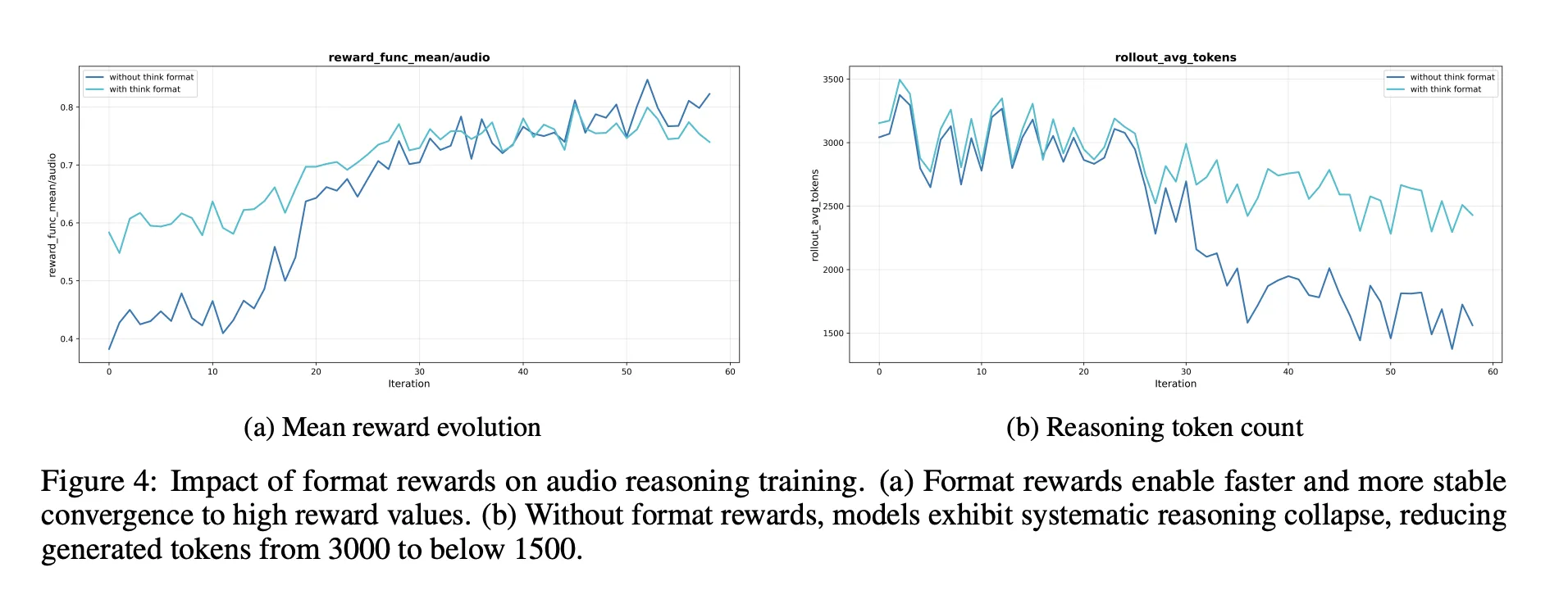
- Inference format bonus is necessary. Without it, reinforcement learning tends to shorten or eliminate thought chains, thereby lowering audio benchmark scores.
- Reinforcement learning data should be for problems of moderate difficulty. Choosing 8-point passing questions in the middle can provide more stable rewards and maintain long reasoning.
- Without such an option, scaling RL audio data is of no help. The quality of the tips and labels is more important than the original size.
The researchers also describe a self-perception correction pipeline that reduces the frequency of answers such as “I can only read text but not hear audio” in models trained on sound processing. This pair of curated preference pairs uses direct preference optimization, where the correct behavior is to confirm and use the audio input.
Main points
- Step-Audio-R1 is the first audio language model that translates longer chains of ideas into consistent accuracy gains for audio tasks, solving the inverse scaling failure seen in previous audio LLMs.
- This model explicitly targets text-agent inference by using modal inference distillation, which filters and distills only those traces of inference that rely on acoustic cues such as pitch, timbre, and rhythm rather than imagined transcripts.
- Architecturally, Step-Audio-R1 combines a Qwen2-based audio encoder with an adapter and a Qwen2.5 32B decoder to always generate
- In a comprehensive audio understanding and inference benchmark covering speech, ambient sounds, and music, Step-Audio-R1 surpassed Gemini 2.5 Pro and achieved comparable performance to Gemini 3 Pro, while also supporting real-time variants of low-latency voice interaction.
- The training approach combines large-scale supervised chaining of ideas, modality-based distillation, and reinforcement learning with validation rewards to provide a concrete and repeatable blueprint for building future audio inference models that actually benefit from test-time computational scaling.


Editor’s Note
Step-Audio-R1 is an important release because it shifts the chain of thought from liability to a useful audio reasoning tool by directly addressing text agent inference with modality-based inference distillation and reinforcement learning with validation rewards. It shows that when inference is based on acoustic features, test-time computational scaling can benefit audio models and provide benchmark results comparable to Gemini 3 Pro, while remaining open and practical for engineers. Overall, this research work moves the extended consideration of audio LLM from consistent failure modes to controllable and repeatable design patterns.
Check Papers, Repos, Project Pages and Model weight. Please feel free to check out our GitHub page for tutorials, code, and notebooks. In addition, welcome to follow us twitter And don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and subscribe our newsletter. wait! Are you using Telegram? Now you can also join us via telegram.
Asif Razzaq is the CEO of Marktechpost Media Inc. As a visionary entrepreneur and engineer, Asif is committed to harnessing the potential of artificial intelligence for the benefit of society. His most recent endeavor is the launch of Marktechpost, an artificial intelligence media platform that stands out for its in-depth coverage of machine learning and deep learning news that is technically sound and easy to understand for a broad audience. The platform has more than 2 million monthly views, which shows that it is very popular among viewers.
🙌 FOLLOW MARKTECHPOST: Add us as your go-to source on Google.


