OpenAI releases advanced voice-to-speech model and new real-time API features including MCP server support, image input and SIP phone support support
Openai has officially launched Real-time API and GPT-REALTIMEits state-of-the-art voice-to-voice model, uses enterprise-centric features to move real-time APIs out of beta. While the announcement marks a real advance in voice AI technology, a closer examination reveals meaningful improvements and ongoing challenges that would reduce any revolutionary claims.
Technical architecture and performance growth
GPT-REALTIME represents a fundamental transition from traditional voice processing pipelines. Instead of linking separate voice-to-text, language processing and text-to-text models, it processes audio directly through a single unified system. This architectural change reduces latency while retaining the nuances of speech that are usually lost during the conversion process.
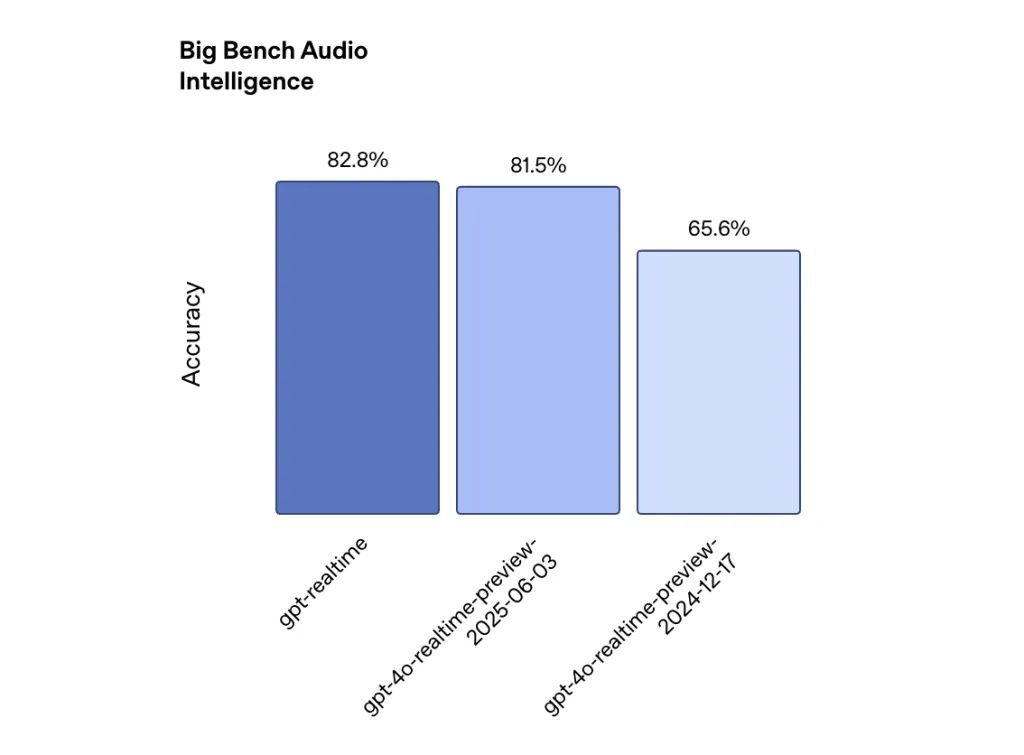
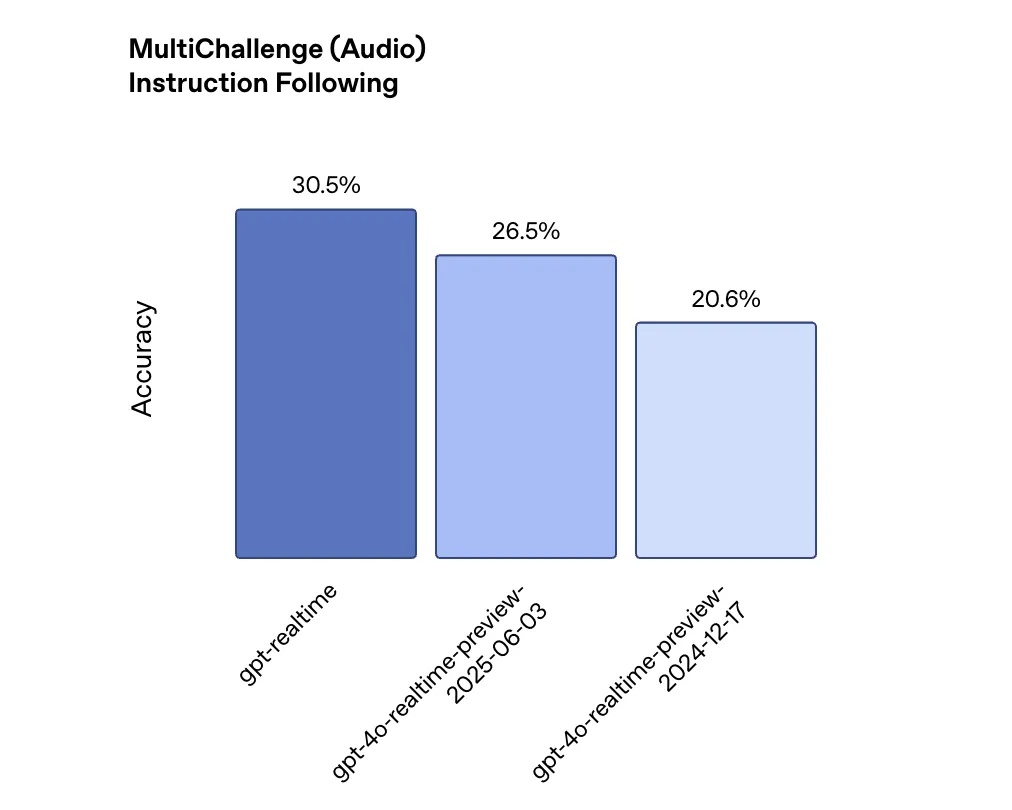
Performance improvements are measurable, but can be incremental. In a large desktop audio evaluation that measures reasoning capabilities, the GPT-REALTIME score was 82.8%, while OpenAI’s December 2024 model was 65.6%, an increase of 26%. For the following description, the multi-key audio benchmark shows that GPT-REALTIME achieves 30.5% accuracy, compared to 20.6% of the previous model. Functional call performance improved from 49.7% to 66.5% of complex Funcbench.
These benefits are huge, but highlight how far AI still has to go. Even the improvement indication below 30.5% suggests that seven out of seven out of ten complicated descriptions may not be properly executed.

Enterprise-level features
Openai obviously prioritizes production deployments and has a variety of new features. The API now supports Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Integrated, allowing voice agents to connect directly to the telephone network and PBX systems. This bridges the gap between digital AI and traditional telephone infrastructure.
Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server support allows developers to connect external tools and services without manual integration. The image input feature allows the model to have grounded conversations in a visual context, allowing the user to ask questions about the screenshots or photos they share.
Perhaps most importantly, for enterprise adoption, Openai introduced Asynchronous function calls. Long-running operations no longer destroy the conversation flow – the model can continue to speak while waiting for the database query or API call to complete. This addresses a critical limitation that makes previous versions unsuitable for complex business applications.
Market positioning and competitive landscape
Pricing strategies reveal Openai’s positive drive to market share. The price per million dollar audio input token and an audio output token per million dollar (20% lower than previous models) is $32, with emerging alternatives down 20% lower than previous models. This pricing pressure shows fierce competition in the voice AI market, where Google’s Gemini Live API reportedly offers lower costs for similar features. NotableCap+2
Industry adoption indicators indicate strong corporate interest. According to recent data, 72% of businesses now use OpenAI products with some ability, and 92% of Fortune 500 companies estimate using OpenAI API by mid-2025. However, voice AI experts believe that direct API integration is insufficient for most enterprises to deploy.
Continuous technical challenges
Despite some improvements, the basic voice AI challenge remains. Background noise, stress variation, and domain specific terms continue to affect accuracy. The model is still struggling with contextual understanding of extended conversations, which is a limitation that affects the actual deployment scenario.
Real-world tests by independent evaluators show that even advanced speech recognition systems face significant accuracy degradation in noisy environments or with multiple accents. While direct audio processing by GPT-RealTime may retain more voice differences, it does not eliminate these potential challenges.
While the delay has improved, it remains a focus on real-time applications. Developers report that achieving response times below 500ms becomes difficult when a proxy needs to execute complex logic or interfaces with an external system. The asynchronous function call function solves some solutions, but does not eliminate the basic tradeoff between intelligence and speed.
Summary
OpenAI’s real-time API marks the tangible (if incremental) move forward in voice AI, introducing a unified building and enterprise capability that can help overcome real-world deployment barriers and combine competitive prices to signal an institutional market. While the model improves benchmark and pragmatic complements (such as SIP phone integration and asynchronous feature summons) that may accelerate adoption in customer service, education, and personal assistance, there are persistent challenges surrounding imperfect conditions around imperfect conditions, which clearly shows that it is clear that this is truly natural, produced sound AI is still in progress.
Check Technical details are here. Check out ours anytime Tutorials, codes and notebooks for github pages. Also, please stay tuned for us twitter And don’t forget to join us 100K+ ml reddit And subscribe Our newsletter.

Michal Sutter is a data science professional with a master’s degree in data science from the University of Padua. With a solid foundation in statistical analysis, machine learning, and data engineering, Michal excels in transforming complex datasets into actionable insights.


